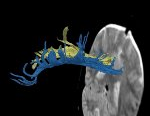
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) is a relatively new imaging technique that can be used to evaluate white matter in the brain. Using DTI, the orientation and direction of white matter fiber tracts can be visualized and quantified (see Figure below which shows visualization of white matter fiber bundles… read more →
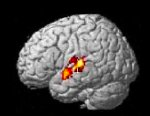
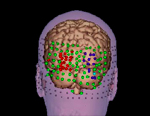
Activation data from fMRI experiments have become an indispensable tool for testing hypotheses concerning the functional roles of brain structures during controlled experimental tasks. To test hypotheses linking anatomical abnormalities with clinical as well as neuropsychological symptoms in schizophrenia, work in the PNL has recently focused on the… read more →
Our group is also interested in the development of new techniques to better characterize brain morphometry, including Poisson’s equation (Haidar et al., 2006), the Laplace-Beltrami Spectrum (Niethammer et al., 2007), Level-set based Shape Morphing (Riklin-Raviv et al., 2014), and methods specifically designed to study the geometry of white… read more →
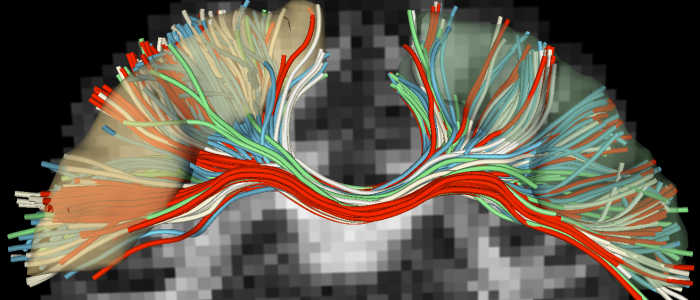
The advent of diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging has provided the opportunity for non-invasive investigation of neural architecture. Using this imaging technique, neuroscientists can determine how neurons originating from one region connect to other regions and how well-defined those connections may be. For such studies, the quality of… read more →
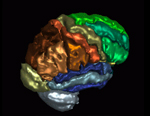
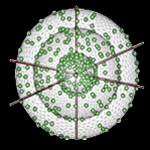
Learning neuroanatomy can be difficult because of the tremendous amount of detail and complexity in the interrelationships among neuroanatomical structures. The use of three-dimensional (3D) anatomic models (or atlases) can greatly facilitate the learning of anatomy because they provide the student with important information about not only the shape… read more →
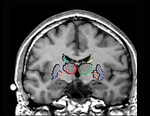
Our group has shown left-lateralized reductions in MR volume of the amygdala-hippocampal complex and parahippocampal gyrus, regions important to verbal memory and associations, and areas that are highly intercorrelated with each other and with the superior temporal gyrus (see the “Projects” section entitled “Chronic Schizophrenia”). These findings suggest that damage… read more →
The quantitative analysis of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data to examine anatomical brain structures is a fundamental component in the assessment of structural brain abnormalities. The method currently used for analyzing brain structures involves a laborious manual tracing of the contours of anatomical structures derived from MRI scans. The… read more →
Diffusion MRI (dMRI) has the ability to detect white matter abnormalities in-vivo by quantifying the water diffusivity that is directionally restricted by barriers such as axonal membranes, myelin and cell packing. In dMRI, the challenge is to describe the 3D probability density function (often referred to as the… read more →
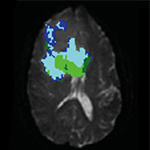
Free-water imaging is an analysis method for diffusion MRI data, which separately models the contribution of extracellular free water and water that is in the vicinity of cellular tissue. Using free-water imaging increases the precision of conventional metrics such as FA and Trace, and quantitatively estimates the degree… read more →